SEO for Product Pages: 9 Essentials that Work for E-commerce
An E-commerce marketer has multiple tools at their disposal to help them increase traffic and online revenue. There are search and social media ads, email marketing, and leveraging the latest trends like conversational commerce.
However, search engine optimization is one of the best marketing strategies in the toolkit, as it can provide organic traffic after retailers make just a few optimizations.
To decide where to get started, SEO for product pages is the most important part of E-commerce SEO, as these pages show up in searches of those interested in making an immediate purchase.
Let’s dive into the most important aspects of E-commerce product page SEO.

Role of Product Pages in E-commerce SEO?
There are three main ways leads find your website pages on Google:
- Your blog articles are found from informational searches. These come from people only looking for information and don’t have a high purchase intent.
- Your home page is found via navigational searches. These people are looking specifically for your brand and probably already know you.
- Your product and category pages are found from transactional searches. These people don’t know about your business yet and want to buy something.
That’s why SEO for product pages is the most important aspect of search engine optimization for E-commerce stores. They attract new customers to your store. Since many of these shoppers are interested in making a purchase the product page can convert them with good visuals, descriptions, and user-friendly navigation.
Investing in product page SEO means you’ll get an influx of new leads who don’t need nurturing, who, in turn, convert on the spot and drive your sales.
SEO Product Page Essentials
Before you optimize product pages, make sure your technical optimization is up to Google’s standards. Check your website with the Lighthouse tool, improve Core Web Vitals if needed, and double-check crawlability and website security. Check out other online shopping problems that are easy to eliminate.
To further enhance your technical SEO, ensure that your website’s URL structure is clean, concise, and user-friendly. Avoid using unnecessary parameters and focus on creating SEO-friendly URLs that are easy for both users and search engines to understand. Implement proper redirects to prevent broken links and ensure smooth navigation. It’s also essential to check your XML sitemap for any errors, ensuring it’s up-to-date and submitted to Google Search Console. You can hire technical SEO consultants to guide you through the best practices and help optimize your site’s performance. Additionally, leverage hreflang tags if you have a multilingual website, ensuring that search engines show the correct version of your pages to international users. Lastly, monitor your site’s health regularly with tools like Google Search Console to detect issues like crawl errors and indexing problems before they impact your rankings.
You’ll also have to do link-building by submitting your site to business directories, writing guest posts, and distributing your content. This will increase your site’s authority in Google’s eyes and increase the odds of your product pages ranking higher in SERP.
With that said, here are the nine things to enhance your product pages and gather more organic search traffic.
Keyword Research
The first step towards optimizing a product page for search engines is finding the right keywords. Keywords are phrases Google users typically use to find the products to purchase.
A single product page can be found with multiple keywords. For instance, a product page for a handheld fan can be found with the following keywords:
- Handheld fan
- Personal fan
- Portable fan
- Battery powered fan
- Mini fan
- Fan that runs on batteries
- Handheld electric fan
- Handheld cooling fan
Your job in this step is to find a list of keywords that would represent your product pages. The more relevant the keywords are, the more traffic it can potentially attract. How do you do that? The fastest way is to use a specialized SEO tool. For instance, the SE Ranking keyword search tool can provide thousands of suggested keywords along with important metrics like keyword difficulty, search volume, and search intent.
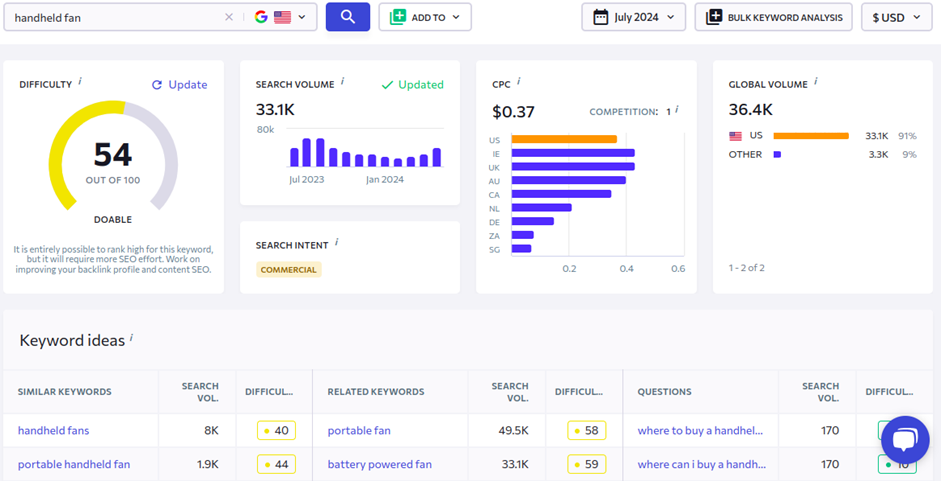
The last one is especially important—you want only commercial and transactional keywords to represent your product pages. Users with informational queries will be disappointed because they are searching for information, not a product.
If you have already done keyword research before and want to find more similar keywords for a specific product page, you can input the keyword manually and go from there. You can also import your keyword list into the tool to do it in bulk.
You can also get the list of keywords you can start working with by exporting a performance report from Google Search Console, or your product list from the CRM.
Once you have a list of keywords, group them and assign them to individual product pages.
Product Page Content Optimization
Once you have that list grouped, optimize product pages for these keywords. Look up which keyword in the group has the most search volume and use it as the main keyword.
Now, you’ll have to add your keywords to the following places on your product page.
- Product Title: contains the main keyword and combinations with other keywords with high search volume.
- Meta Title Tag: contains the main keyword and combinations with other keywords with high search volume.
- Meta Description Tag: contains the main keyword and is aimed towards convincing users to click on your link in SERP.
- Headings: contain the most prominent keywords, H1 contains the main keyword, and other headings contain supporting ones.
- URL Slug: contains the main keyword.
- Product Description: contains all keywords in the list in an authentic way.
The most important thing when it comes to optimizing the product description is not to overoptimize it.
First and foremost, you want your description to be informative for the user.
Add keywords only where they make sense, and don’t add more than a couple of instances of the main keyword. You can add other keywords just once
Also, add user-generated content to the pages. Having customer reviews on the product page adds unique content and updates the page, both of which are good for SEO.
It may be hard to optimize hundreds of product pages that an E-commerce site typically would have.
If you have to prioritize, start with the low-hanging fruit. Find pages with the potential to rank well—pages in the top 20 for a keyword with low keyword difficulty.
Image Optimization
Keyword-optimize your image files. To do this, add the main keyword to the alt tag of the image and to the image file name. The alt tag should describe the image, so don’t stuff it with keywords.
There are other areas for optimization when it comes to images. First, keep the size of the images to a minimum. Large image files take a while to load and can slow down the page loading time. This negatively impacts both user experience and SEO for product pages.
Also, try to have the images fit the optimal aspect ratios for appearing on SERP. Your images can appear in rich results and the image search feature.
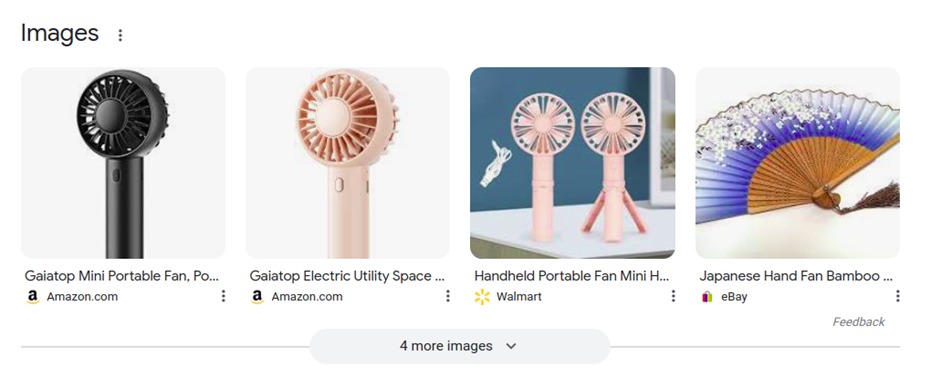
The best aspect ratio for product images is 1 to 1, with resolutions ranging from 300 x 300 to 1200 x 1200. Make sure the image still looks good when it’s resized in SERP.
Video Optimization
Sometimes, videos can appear in search results, too.
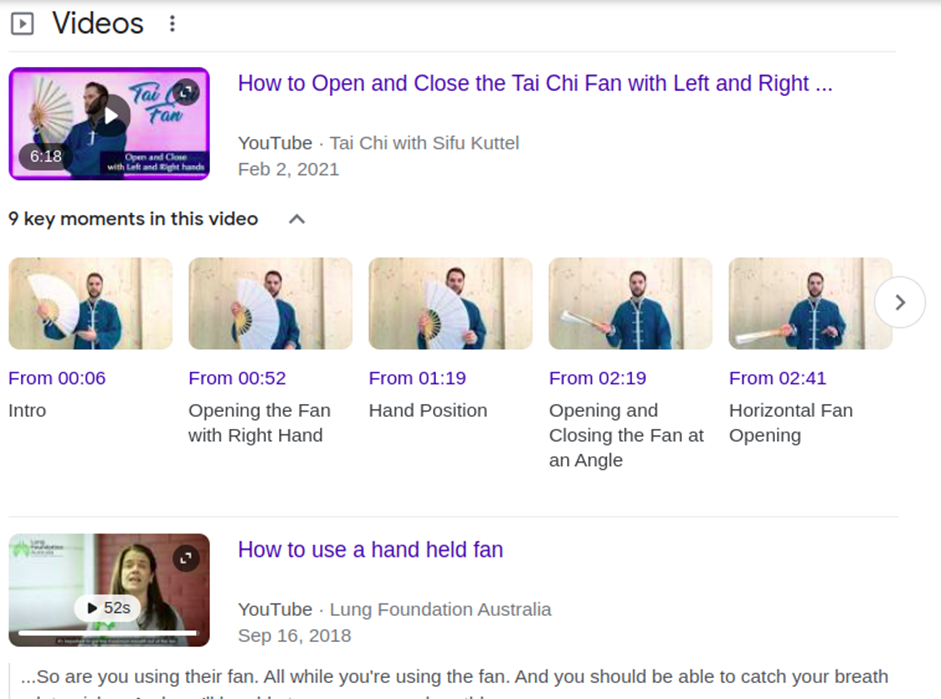
Mostly, videos will appear in informational or commercial searches—searches with the intent to find information on using a product.
The majority of videos linked here are hosted on YouTube. If you have a YouTube channel, make sure to add keywords to the title and description of the video.
If you’re hosting the video on your E-commerce site, compress the video for faster loading, add VideoObject Schema, and create a captivating thumbnail.
Good ideas for product page videos are unboxing and product guides.
Helping Features
Adding helpful widgets relevant to your product can help both SEO and user experience. For instance, a calculator for vitamin pills, an AI try-on feature for fashion or makeup products, or a size-fitting assistant.
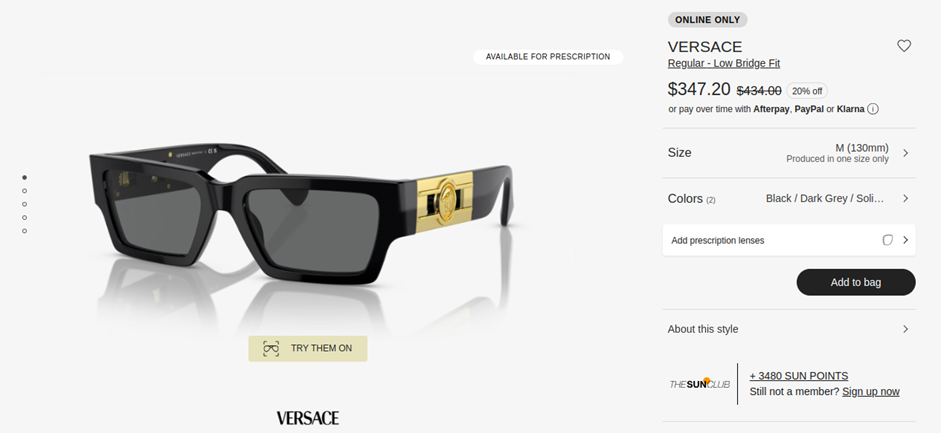
The impact on the UX is obvious. In terms of E-commerce product page SEO, it can increase the number of links to your product pages because people love to share handy widgets like that.
Structured Data for Product Pages
SEO is not only about optimizing the page to appear higher in search. It also includes optimizing SERP design. This includes creating a title and description that entices users to click as well as creating rich results like these.
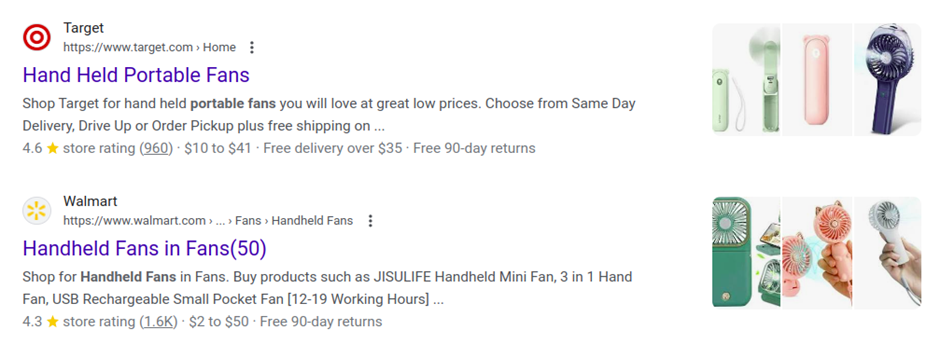
To have your product page display images of the product, rating, and price, use structured data or Schema markup. It’s a JSON-LD document that includes all the relevant information about your product.
There are several ways you can create structured data.
- Write the JSON code yourself.
- Use an AI tool to create it.
- Use Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper.
- Use a plug-in native to the E-commerce platform you use.
Make sure to check your product pages with Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool before you make the changes live.
Avoiding Cannibalization
Often, E-commerce stores have dozens of nearly identical products, like different color variations of the same handheld fan. If you create a different page for each of them, it won’t be good for product page SEO, as Google doesn’t like duplicate content. These pages are also likely to cannibalize each other—your pages will compete with each other in SERP.
To avoid this, don’t create unnecessary pages and group similar products on one page.
Sometimes, you have to, though. For instance, when there’s a sizeable search demand for “pink handheld fan” and “white handheld fan,” and you want to serve your audience by showing exactly what they want.
In this case, make sure to write unique product descriptions for these pages and point a canonical link to the main product page.
Mobile-Friendly Design
As over 50% of internet traffic is mobile, Google prefers to rank mobile-friendly pages higher in SERP, especially so for mobile searches. You can check how well your website works on different devices with the Chrome Inspect tool. It lets you change between different devices and aspect ratios.
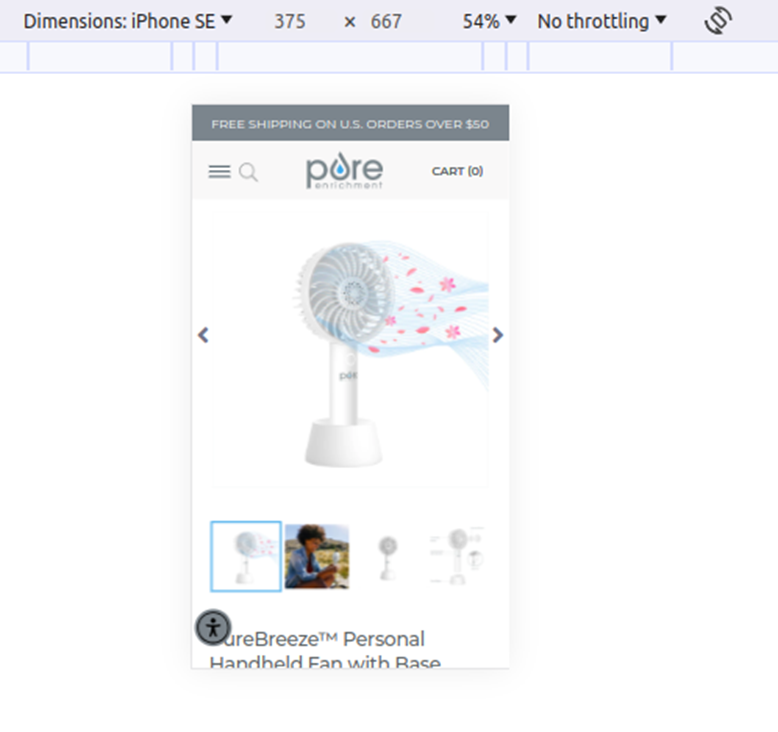
Run a Lighthouse report on the page to see how well it loads on mobile platforms. It will show a brief analysis of performance problems.
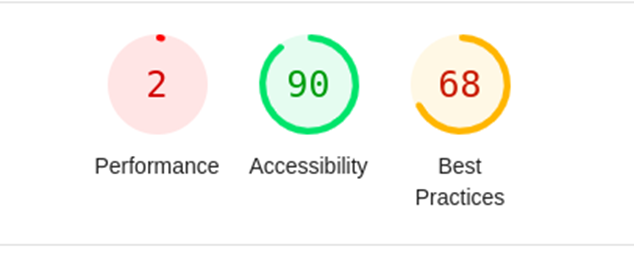
To improve performance, minimize JavaScript execution time, remove time-blocking resources, and minimize JS and CSS on the page.
If you’re using an E-commerce platform like Shopify, try testing performance with and without plug-ins, especially older ones.
Internal linking
The only way Google can know a page exists is if a link points to it. You need to create internal links to your products to help them get discovered and indexed. A lot of internal links pointing to a specific page will signal to Google that the page is more important than others.
To help with crawlability, create a user-friendly linking system. Link to your product pages from:
- Navigation menu
- Sitemap
- Category pages
- Other product pages
The last one can also improve your site’s UX and average sale value, as they often are in the form of product suggestions.
Use a plug-in to create those product suggestions automatically for each product page.
If you want to improve the SEO of a specific page, for instance, a page that has the potential to rank well for its keywords, leave additional links from your website.
Your best options are adding a link from the homepage in the form of a banner or a navigation menu link, then adding links from your blog content. Prioritize it in product suggestion sections or add a bestsellers section.
Summary
Optimizing product pages for search doesn’t take as much work as off-page SEO. Follow this guide and see how the positions change in a few weeks when the page is indexed.
Change your approach as you track the key metrics and work closely to optimize your pages, starting with the ones that have the most potential. Once you find the right SEO approach to your specific market based on these pages, expand it to the rest of the site.
Author:

A dynamic Digital Marketing Manager at SE Ranking, brings a wealth of expertise in SEO, digital, and content marketing. She believes in using content to build strong brands.
Outside of work, Kelly travels the world, learns new marketing techniques, and blogs about her adventures.

